| ADRK |
| Allgemeiner Deutscher Rottweiler-Klub e.V. |
X-Ray
Inhaltsverzeichnis
X-ray-Portal
Since August 2010, the web-based research portal vetsXL for the GRSK e.V. is completely available. Veterinarians can upload the images, associations can manage the images, and a powerful DICOM viewer with corresponding measuring instruments is available for the experts. This presentation shows the procedure for veterinary surgeons, associations and consultants. Further information can be found here (only in German).
If you do not use the portal, please send in pictures and documents together to the ADRK office:
ADRK
Postfach 400222
32400 Minden
Optimal Positioning
Dr. K. Amort
The optimal positioning of the elbows includes a mediolateral projection with moderate flexion (40-70%). The proximal and dorsal contours of the anconaeus processus (black arrow) must be clearly visible.
Extreme flexion of the joint should be avoided: The medial coronoid process of the ulna should not be superimposed on the distal humerus and skull cortex.
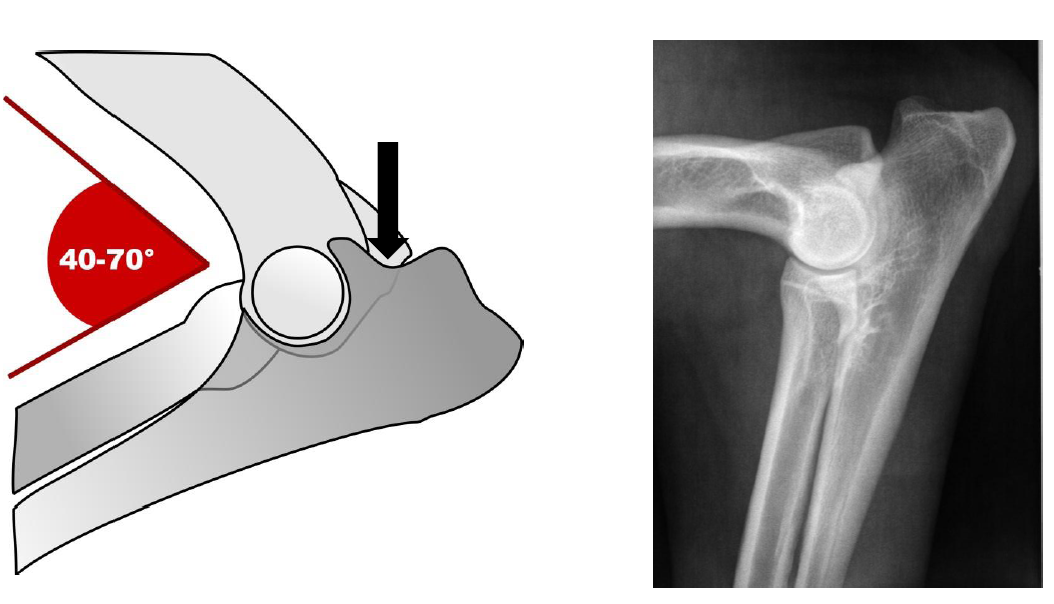
Figure 1 shows the optimal positioning of the bent elbow in a schematic drawing and on a Medio-Lateral X-ray.
Additional x-rays of the elbows are recommended. Positioning includes (approximately) 15° pronation (rotation of the limb toward the medial side) to mark the medial crown process (Figure 2: White Arrow) and indicate the contour of the Distal Humeralis Roll.
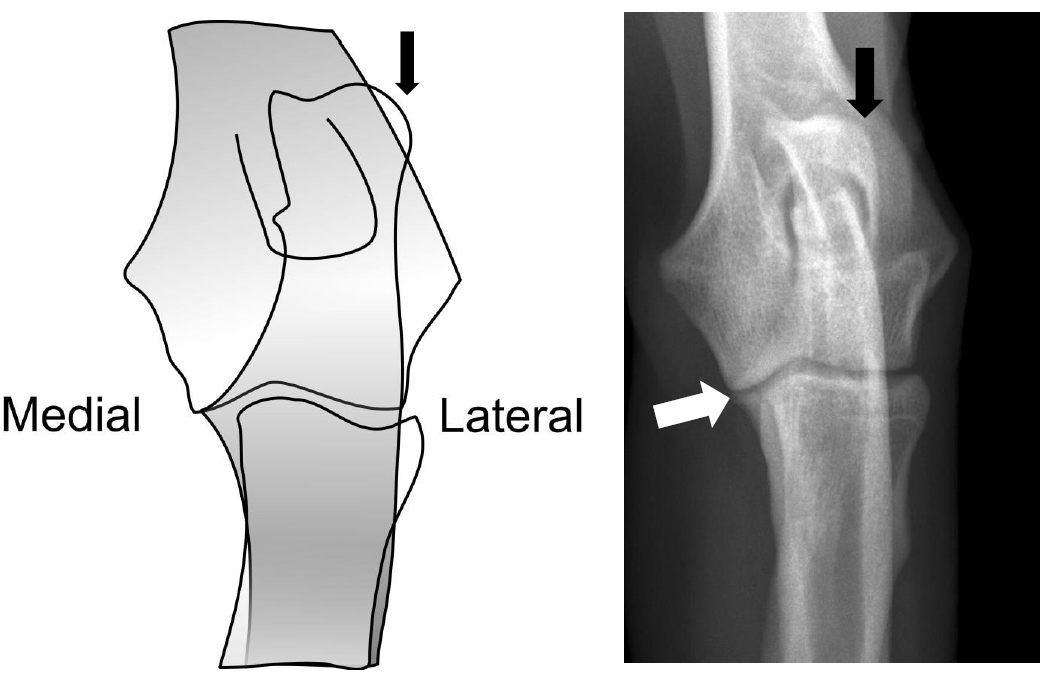
Figure 2 shows the optimal positioning of the elbows on an X-ray image. The proxolateral contour of the olecranon has rotated to the lateral cortex of the distal humerus (black arrow).
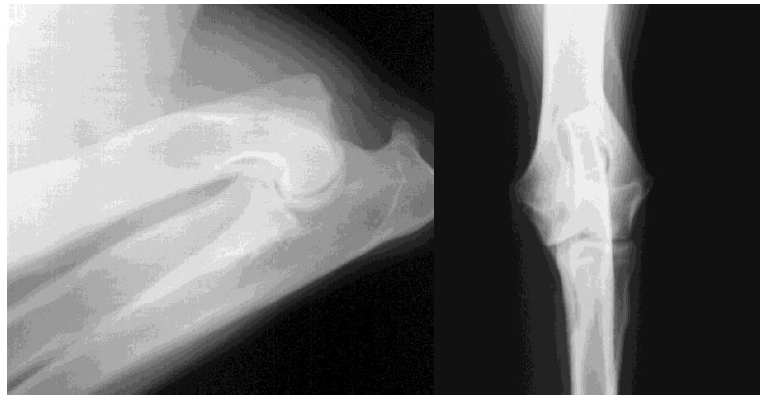
Figure 3 shows the most common shortcomings. X-ray on the left: Extreme diffraction and supination leads to limited assessment of the apex of the skull of the medial coronoid process. X-ray right: Pronation craniocaudal leads to limited assessment of the medial joint.
For the assessment of hip dysplasia, at least one correctly positioned x-ray of the hip is recommended (Figure 4).
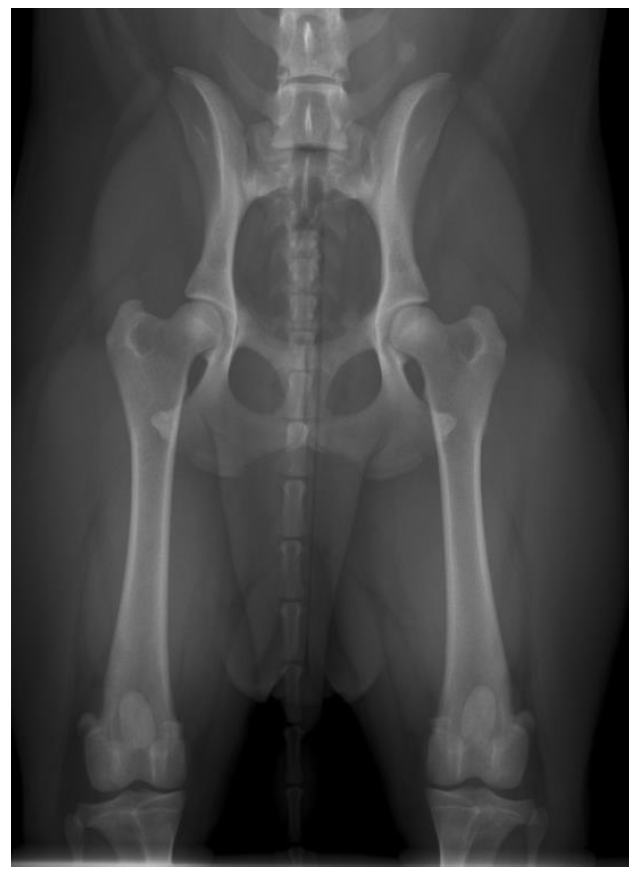
Figure 4 shows symmetric pelvis, hind legs are parallel and widened (same horizontal diameter at both sides). The patella is visible between the two legs. The skull contour of the sacrum should be shown.
Technique
For an optimal quality of digital X-ray images high resolution and high contrast are essential. An accepted and widely used image format is DICOM. In exceptional cases, X-rays in other formats are also possible, but in good quality. X-rays that are overexposed, inaccurate and out of focus are rejected.
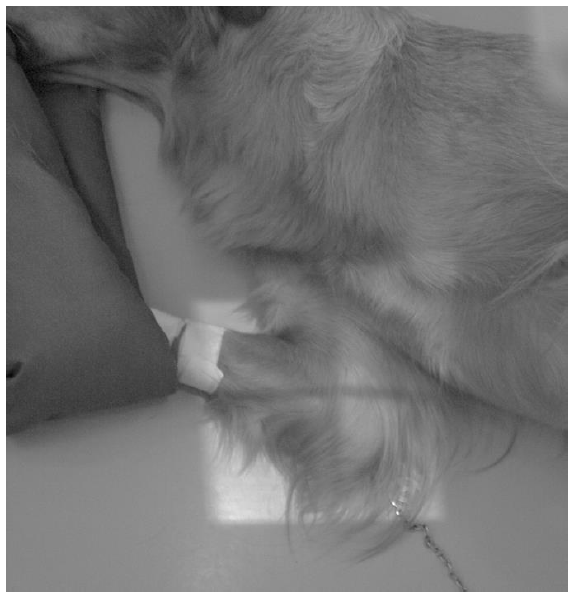
Figure 5 shows a mediolateral x-ray image in flexion.
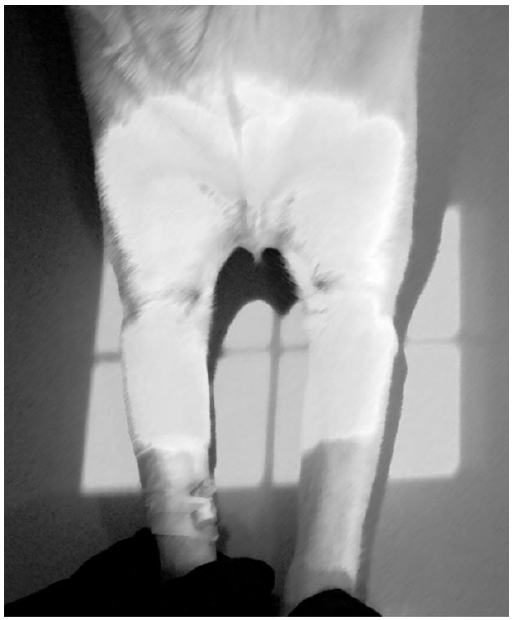
Figure 6 shows a craniocaudal X-ray image in pronation
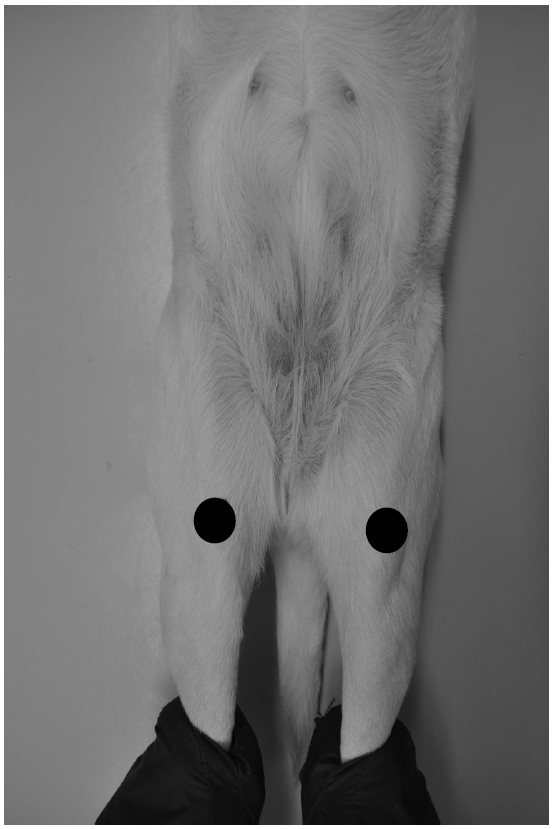
Figure 7 shows the X-ray image of a ventrodorsal hip (black dots show the position of the kneecap).
Contact Dr. Amort for further details and questions: kerstin.h.amort@vetmed.uni-giessen.de









